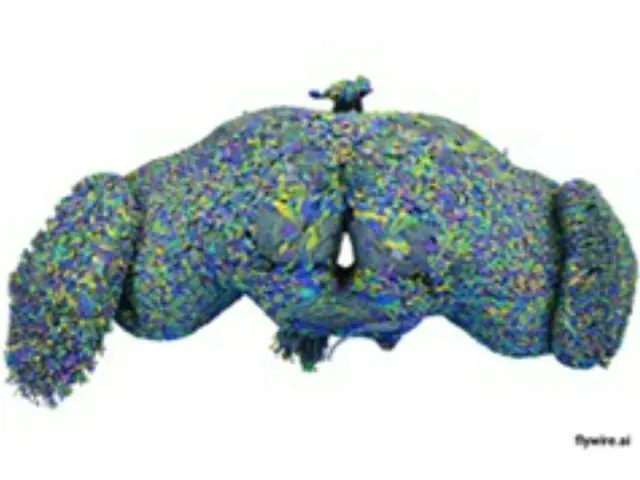
The research was led by researchers from the university, including Dr. Lee Gi-seok of Zeta AI, which develops artificial intelligence (AI) platforms, and Bae Jun-hwan of the Institute of Basic Science at Seoul National University.
The researchers included Dr. Kim Jin Seo, professor at the Department of Life Sciences at Sungkyunkwan University. Drosophila shares about 70% of its genes with humans, including genes related to learning and biological rhythms.
Three-quarters of genetic diseases manifest themselves in ways similar to those in humans, and mapping the brain in fruit flies is important for understanding diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
In this study, the brains of fruit flies were removed, cut into nanometer-level slices, and 3D images were made using an electron microscope. The electron microscope was used to segment synapses, and AI was used to identify the substances that connect them and the branching points.
Dr. Bae Jun-hwan said, "Drosophila has advantages for mapping animal brain functions, but it has limitations compared to higher organisms.
"I would like to actively conduct research on higher organisms in the future, and hope that this will help humans overcome diseases."
2024/10/07 08:47 KST
Copyrights(C) Edaily wowkorea.jp 101